For centuries, scientists have been driven by curiosity and ambition to explore the unknown. What we know today is only a fraction of what there is still to learn about our world. While countless discoveries have been made, there are still many unsolved mysteries within the realm of science that has yet to be uncovered or explained. This article will explore some of these unsolved science facts.

Are parallel universes a reality? Many scientists believe that there are multiple universes, or an infinite number of separate realities, all existing alongside each other in the same space and time. The idea of parallel universes has been around for decades and its implications are mind-boggling.
The theory comes under the umbrella of quantum mechanics, which states that any particle can be in more than one place at once. This means that every decision we make might exist in different versions of the world due to our choices creating alternate realities. Some experts suggest this could mean that anything possible exists somewhere else, even if it hasn’t happened here yet. It also suggests that everything we experience is actually happening in another universe at the same time.

Why do we sleep? Although we know that a circadian clock puts people on a sleep/wake cycle, we don’t completely understand why. We spend roughly a third of our lives sleeping, which is when our bodies repair tissues and carry out other maintenance tasks. Why do we need to sleep when other organisms don’t? There are a few different theories, but none seem to provide a convincing response. According to some theories, others who must stay more awake can rest and recover in different ways without entirely sleeping. In contrast, others who can sleep have evolved the capacity to conceal from predators. While they still don’t fully understand why humans do it, scientists are beginning to understand its significance and how sleep affects vital processes like brain development.

What happens inside a black hole? Black holes have long been a source of mystery and fascination. They are places in space where gravity is so strong that not even light can escape, yet they remain largely mysterious to us. What happens inside a black hole? To answer this question, we must first understand what a black hole is and how it is formed.
A black hole forms when matter collapses under its own gravitational force, creating an area of such intense gravity that nothing within the vicinity, including light, can escape its pull. Anything that enters the boundary of the black hole – known as the event horizon – will never be able to escape due to the extreme gravitational forces at work. As one approaches closer and closer to a black hole’s center – known as its singularity – space-time warps infinitely until time itself ceases to exist.

How do animals migrate? In order to avoid shifting seasonal temperatures and the diminishing resources that come with them or to find mates, many animals and insects migrate throughout the year. How can these migrations, some of which might cover thousands of kilometers in one direction, find their way there and back repeatedly each year? Various animals employ various types of navigational aids, and some of them can even use their own magnetic fields to act as compasses. Scientists are still unsure of how this ability arose or how wild animals are able to predict their exact location season after season.

What Lives in the Ocean’s Twilight Zone?The ocean’s twilight zone is one of the least explored areas on earth, yet it is teeming with life. Located 200 to 1,000 meters below the surface, this unexplored ocean region contains a plethora of unique creatures that have adapted to living in extreme darkness and pressure. Scientists are only beginning to uncover what lies in the depths of the twilight zone and its mysterious inhabitants.
This part of the ocean is home to various organisms, from unusual fish species like hatchet fish and lanternfish to fierce predators like dragonfish and cookie-cutter sharks. As well as being their habitat, these deep-sea creatures use their environment for protection by using camouflage or bioluminescence for hunting prey. The twilight zone also houses invertebrates such as squid, octopuses and even jellyfish, ancient species that can survive in extreme conditions.
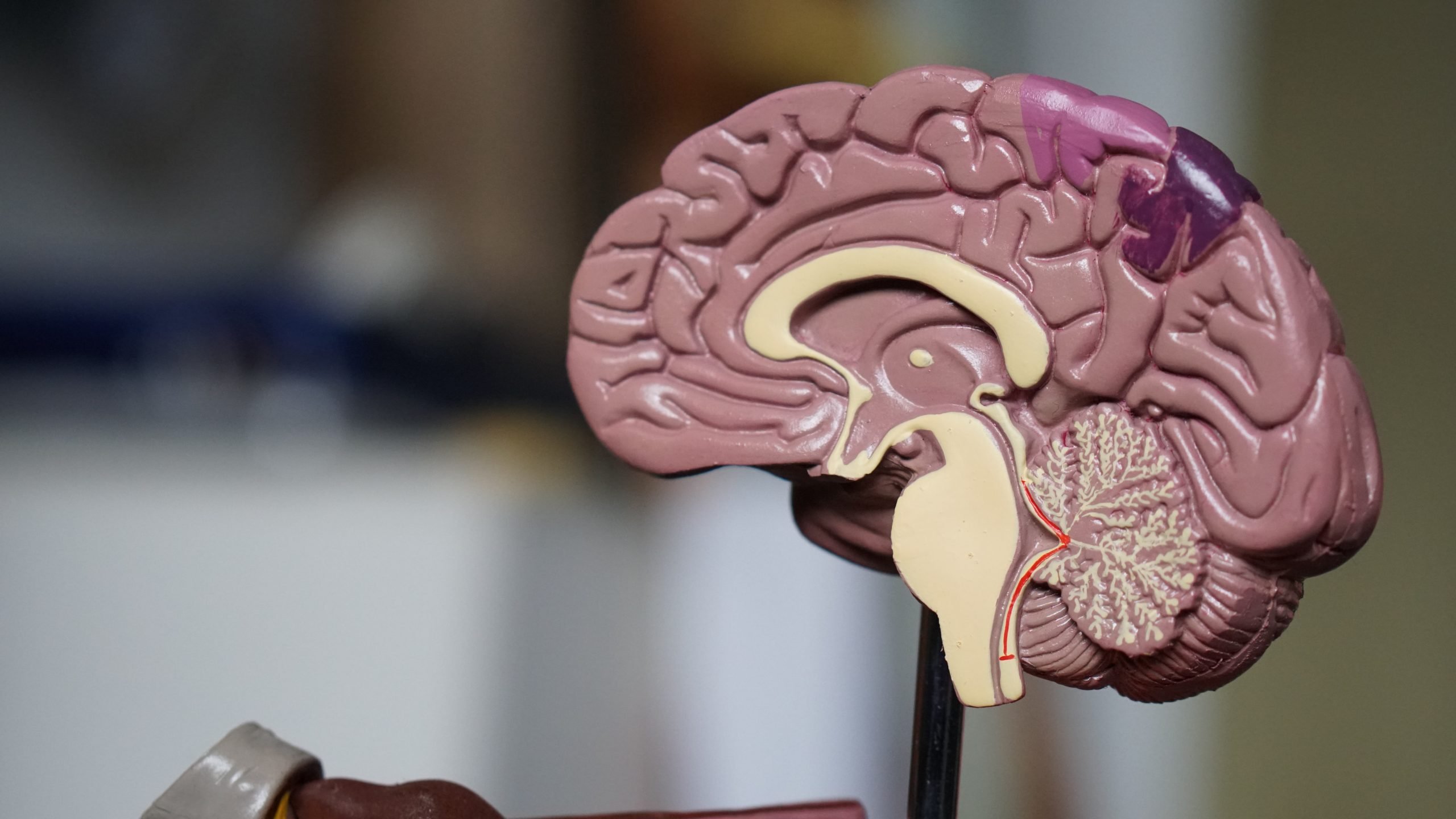
What causes Alzheimer’s? Alzheimer’s disease is a form of dementia, a neurological disorder that affects memory and other cognitive abilities. It is one of the most common forms of dementia in older adults and can be devastating to those living with it. While research continues to better understand Alzheimer’s disease, there are still many unknowns about its cause.
Experts believe that age and genetics may play an important role in developing Alzheimer’s disease. Age is the greatest risk factor for Alzheimer’s, as most people with the condition are over 65 years old. A family history of Alzheimer’s or other types of dementia also increases risk, particularly if someone has a parent or sibling with the condition. Additionally, scientists have found links between some genetic mutations and increased risk for developing late-onset Alzheimer’s – although only a small percentage of cases are linked to these mutations.




