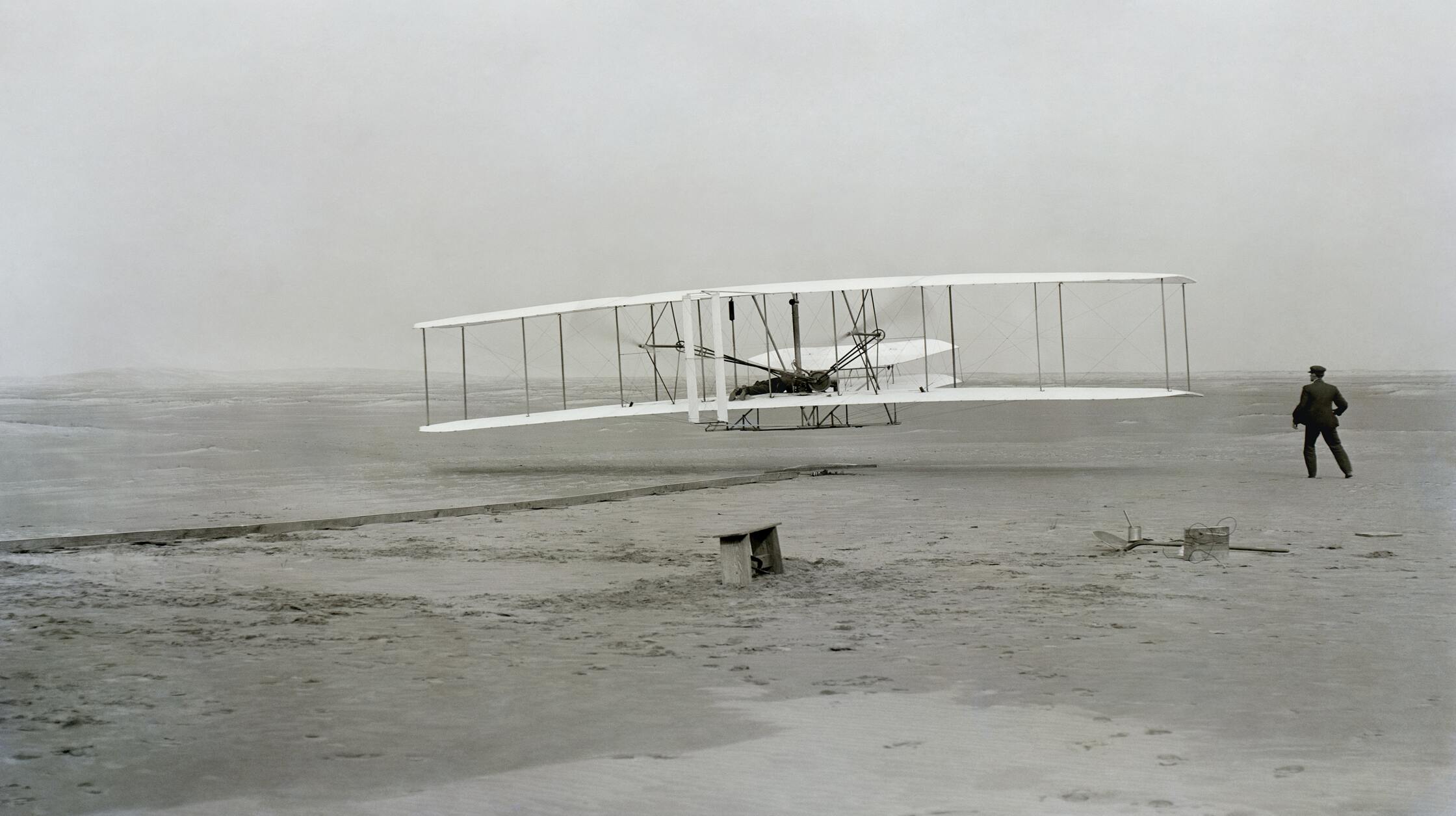
Inventions are a great way to make life easier and more enjoyable. The problem is that most inventions take time to catch on, so we don’t always know about them before they’re too late for us to use them.
We all know that the ancient world was full of inventions, but it is hard to determine which ones were ahead of their time. This blog will explore some of these inventions and how they might have been ahead of their time.
Antikythera Mechanism

The
Antikythera mechanism is one of the most famous ancient greek inventions. It
was a device that, according to recent studies, could have been used as an
orrery and also as a mechanical calculator which might have helped with
navigation by calculating positions of celestial bodies. The name Antikythera
mechanism derives from its discovery on April 17th 1901 at the Antikythera
wreck off Point Glyphadia on the Greek island of Antikythera.
Baghdad Battery
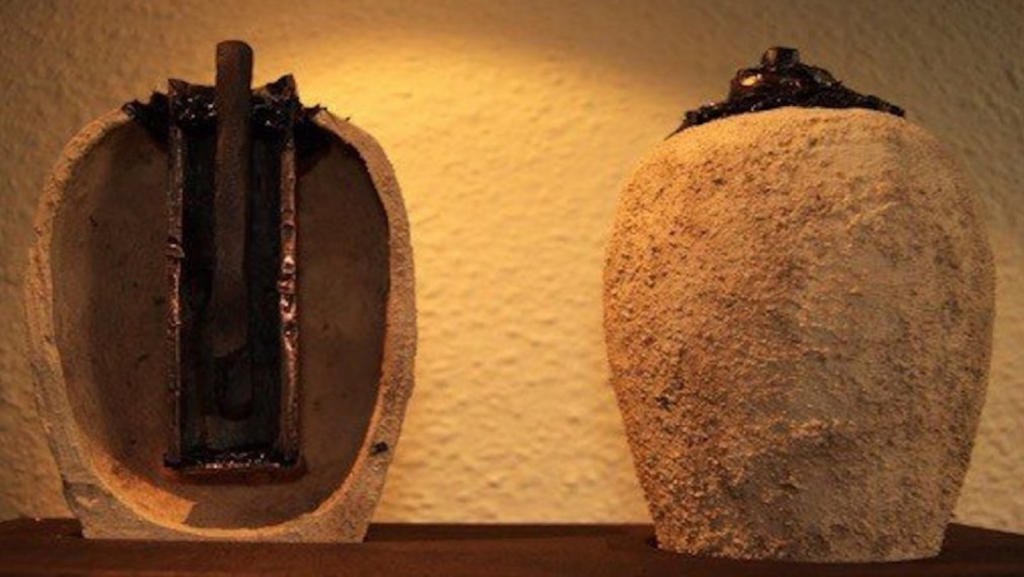

Source: GlobalMarvels
The Baghdad Battery is a popular artifact which was found in Iraq’s capital city of Baghdad, and has been dated back to around 200 BC. This discovery led scientists to believe that it could be one of the first known batteries ever created. It consists of an earthenware pot with a copper cylinder inside, and there are wires made from gold or silver that connect the two metal pieces together.
The artifact, which is believed to be around 2,000 years old, consists of a ceramic pot with an iron rod inside it. It has been speculated that the device may have actually functioned as a galvanic cell and could have had some use in electroplating or even electrochemistry experiments.
Houfeng Didong Yi

In AD 132, Zhang Heng, official court astronomer and historian to the Eastern Han Dynasty, invented the world’s first earthquake detector. Though not as advanced as today’s seismographs (from which we can determine the epicenter and magnitude of an earthquake), the Houfeng Didong Yi could determine the occurrence of the slightest earthquake, as well as its general direction.
The device looked like a big bronze pot, adorned with eight dragon heads and eight toads at the base. Each dragon held a small bronze ball in its mouth, this dropped into one of the toads’ mouths to show the direction of an earthquake. The clang of the ball alerts officials to the shake, which they interpreted as either Heaven’s anger or an imbalance between good and evil.
Damascus Steel
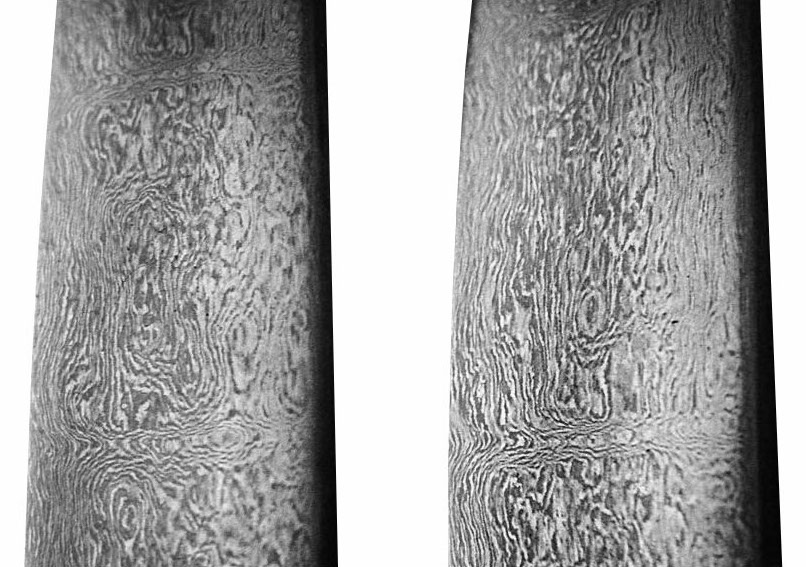
Damascus steel is a type of sword that has been made for centuries. It was first forged in Damascus, Syria and the process to create it is still unknown. The metal is mixed with other metals like copper, nickel, and zinc to give it its distinctive pattern. Bladesmiths usually use this technique because the blades are more flexible than those made from pure steel which makes them easier to sharpen without breaking.
The most famous example of this type of sword would be the Japanese Katana.
Stonehenge
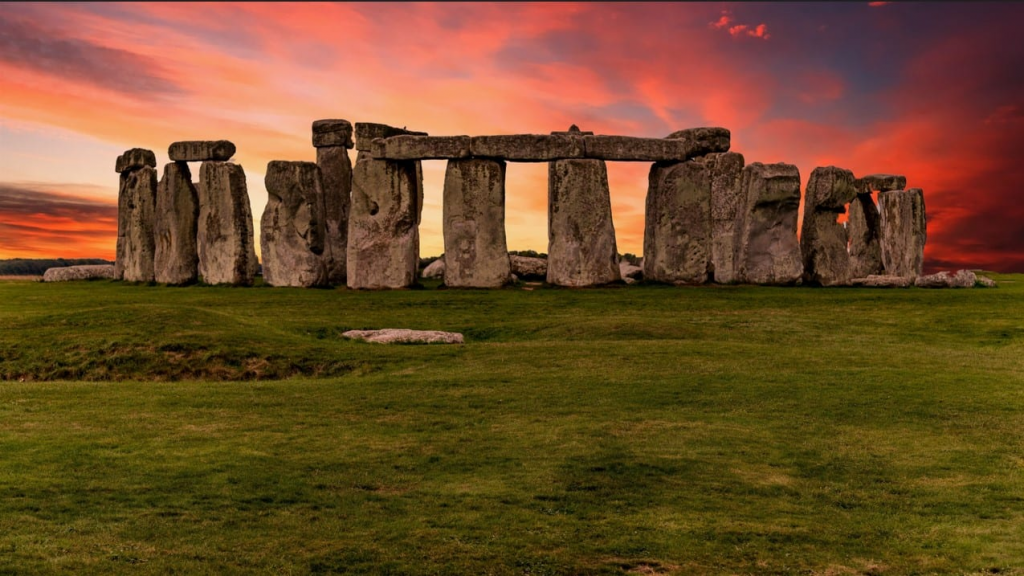

Stonehenge is a large and mysterious stone monument located in Wiltshire, England. It was built between 3000 BC and 2000 BC by the Neolithic people of Britain during their Bronze Age. The stones themselves are mostly made from sarsen, a kind of sandstone that can be found locally to the site. They were dragged here (over 20 miles) along ancient trackways called cursus which date back even earlier than Stonehenge itself – around 2500 BC!
Viking Compass
The Viking Compass is a compass that was used by Vikings. The invention of the compass had many benefits, including navigation and exploration. The Viking Compass helped with navigation because it allowed for better mapping of journeys and gave sailors an idea of where to go in order to find new land or explore the seas. This led to discoveries such as America in 1492 which changed the world forever.
The Viking Compass also played a big role in exploration because it helped create maps which were essential tools for exploring new lands!
The Great Pyramid of Giza
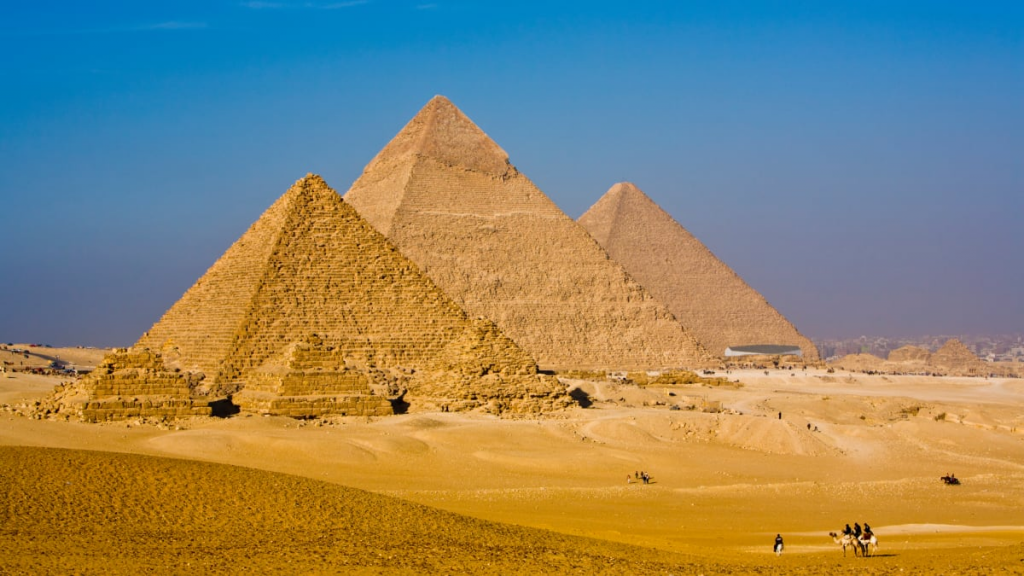

Source: History
The Great Pyramid of Giza is one of the most famous landmarks in the world. It was built by ancient Egyptians and is considered to be a true architectural wonder. Egyptologists say that it took 20 years to build this pyramid, which has been standing for over 4,500 years. The base covers 13 acres and rises up to an enormous height of 480 feet (140 meters).
The Great Pyramid of Giza is
one of the most famous pyramids in the world, and for good reason. It stands as
a symbol for ancient Egyptian culture and engineering ingenuity. The pyramid
was built around 2560 BC to serve as a tomb for Pharaoh Khufu (which translates
to the light shines from him).




