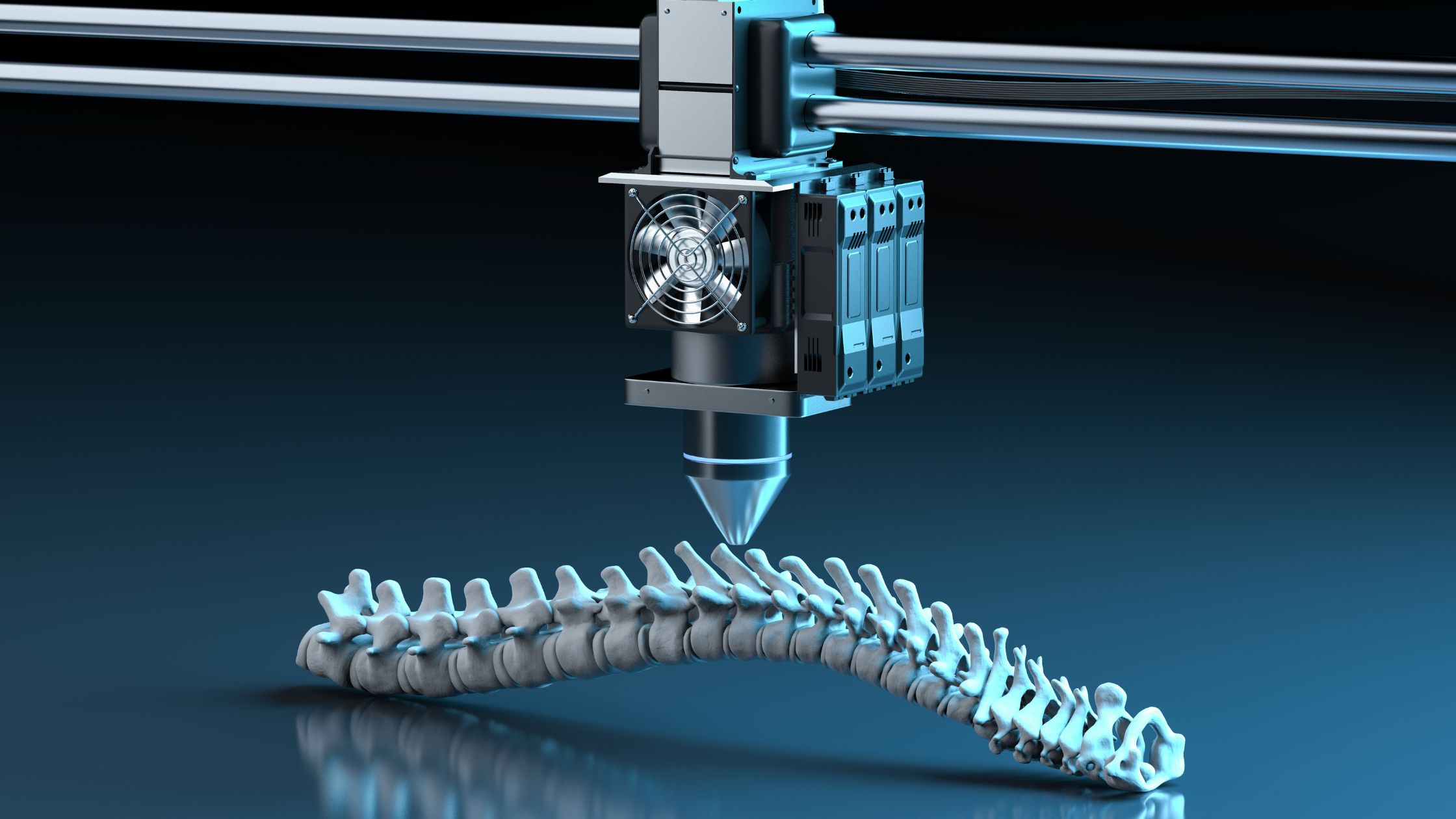
In recent years, the use of 3D printing technology has made significant strides in the field of healthcare. From creating patient-specific prosthetics to the potential of printing functioning organs, the applications of 3D printing in medicine are revolutionizing patient care. This blog will explore how 3D printing is being utilized in healthcare and highlight some of its key use cases.
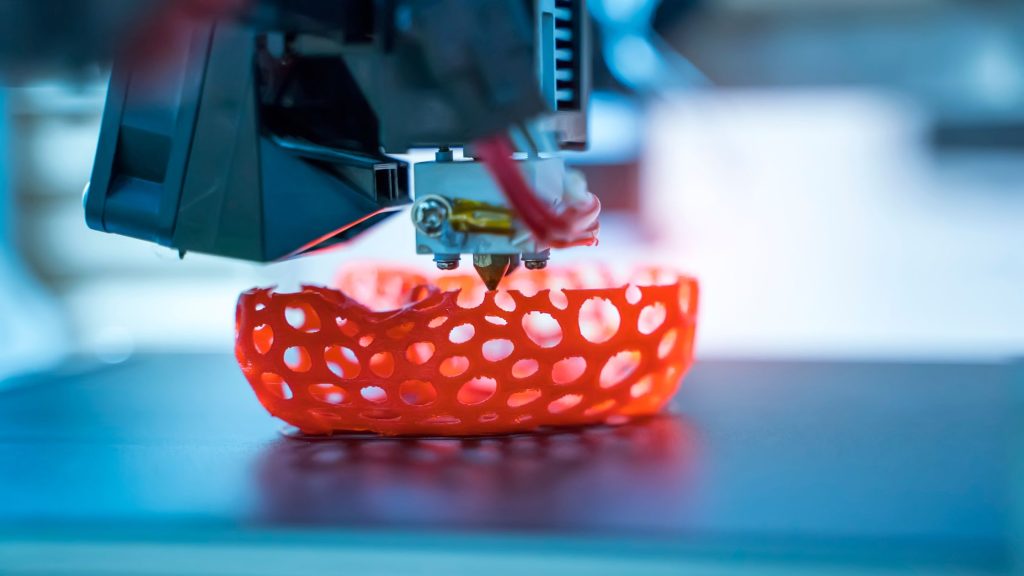

Utilizing 3D Printing in Healthcare: The utilization of 3D printing technology in healthcare is not a mere science fiction concept. Today, healthcare professionals and scientists are leveraging this technology to bring about groundbreaking advancements. One notable application is in the production of prosthetics and orthotics, where FDM printing technology and flexible TPU 3D printing material are commonly employed. TPU offers a balance between strength and flexibility, making it suitable for creating prosthetics that can withstand impact while not restricting mobility. Furthermore, TPU is also used in the development of 3D-printed organ prototypes, which aid doctors in pre-surgery preparation and testing of new surgical techniques.
Use Cases of 3D Printing in Healthcare: Every individual’s body is unique, and 3D printing allows for unprecedented customization in healthcare applications, particularly in the creation of prosthetic limbs and other medical devices.
3D-Printed Medical Prototypes: Surgeons typically rely on scans of patients to plan surgical procedures. However, with 3D printing, doctors can now utilize lifelike replicas of patients’ organs to perform pre-surgery preparations or test unique surgical methods. TPU’s flexible properties make it an ideal material for creating organ prototypes, while rigid TPU can be used to produce prosthetic limb sockets that offer a comfortable fit.
Custom-Built Prosthetics: While prosthetic limbs are not made of organic material, they become an integral part of an individual’s body. Custom-fitted 3D-printed prosthetic pieces offer enhanced performance and functionality. The ability to design prosthetics specifically tailored to each individual’s needs is a significant advantage of 3D printing technology.
NinjaTek® Filaments in Healthcare: NinjaTek’s range of 3D printing filaments finds extensive application in medical settings, addressing the flexible and rigid requirements for prosthetics and realistic organ replications.
- NinjaFlex® is suitable for organ printing, pre-surgery preparations, teaching hospitals, braces for joints, prosthetics, and orthotics.
- Cheetah® is ideal for dental arm clips, braces for joints, prosthetics, and orthotics.
- Armadillo® is well-suited for prosthetic sockets and shells.
- Chinchilla™ is used for prosthetic liners and organ printing, particularly in pre-surgery preparations and teaching hospitals.
FAQs about 3D Printing in Healthcare:
Can organs be 3D printed? Yes, a process known as bioprinting allows for the creation of organs. However, it is important to note that NinjaTek currently does not provide 3D printing materials that are safe for internal use.
Can 3D-printed parts be sterilized? Yes, most 3D-printed parts can be sterilized or autoclaved. However, the ability to withstand sterilization processes depends on the type of material used. For example, NinjaFlex and Cheetah are better suited to withstand heat during sterilization, whereas Armadillo may not be suitable for this purpose.
Conclusion: The use of 3D printing in healthcare is transforming the way medical professionals approach patient care. From customized prosthetics to lifelike organ replicas, this technology enables greater personalization and innovation in medicine. As research and development continue to expand, the potential of 3D